1 May 2017
Study of historic Chilean quake warns of a future tsunami
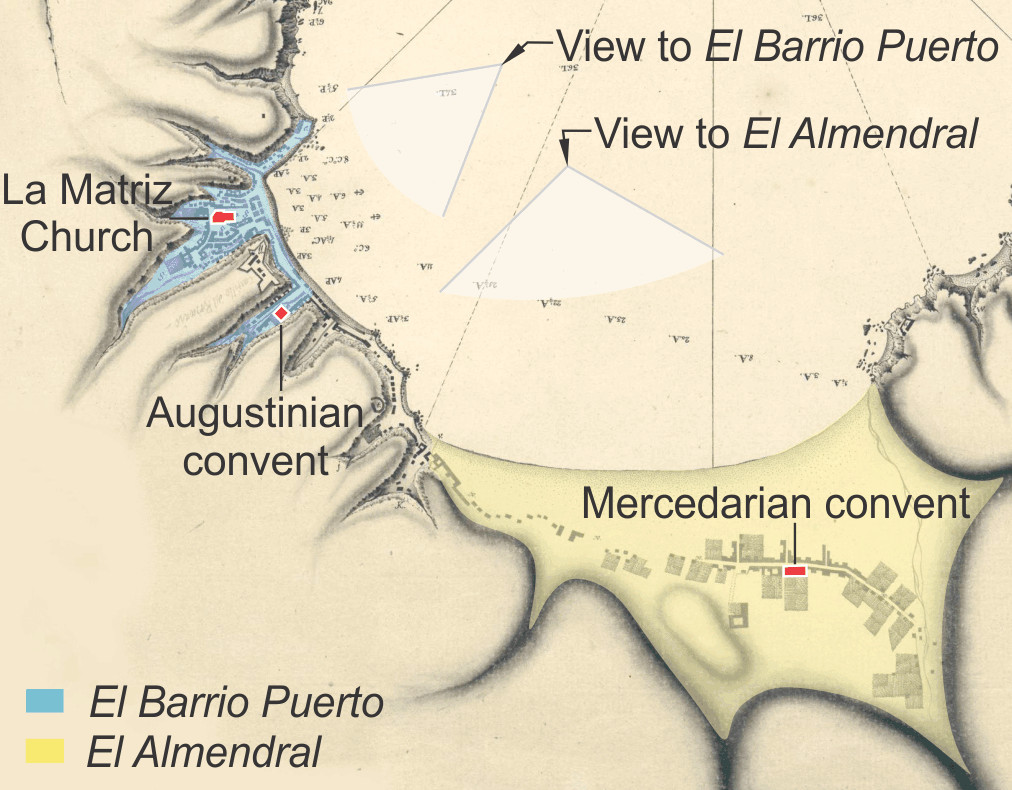
The most populated central region of Chile could be vulnerable to large tsunamis generated by a deceptively moderate kind of earthquake that might be overdue, say scientists who have sorted out the source of an earthquake and tsunami that struck the area 287 years ago. The region is the same that trembled from a magnitude 6.9 earthquake on April 24.
27 April 2017
Glass formed by volcanic lightning could be used to study eruptions
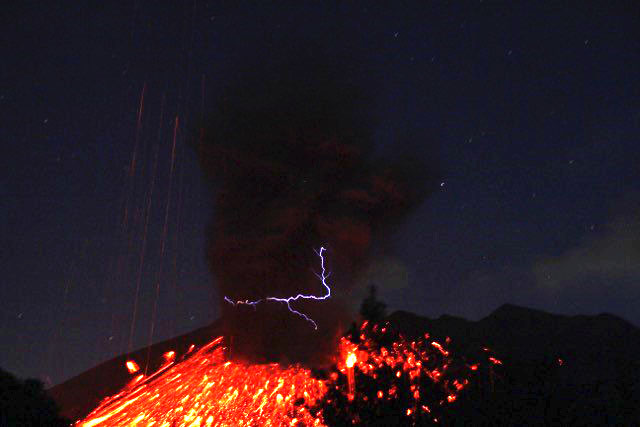

Researchers have developed a method to measure one of the most striking and difficult to measure volcanic features – volcanic lightning – using the tiny glass spheres formed by hot volcanic ash.
26 April 2017
New study challenges long-held tsunami formation theory (plus video)
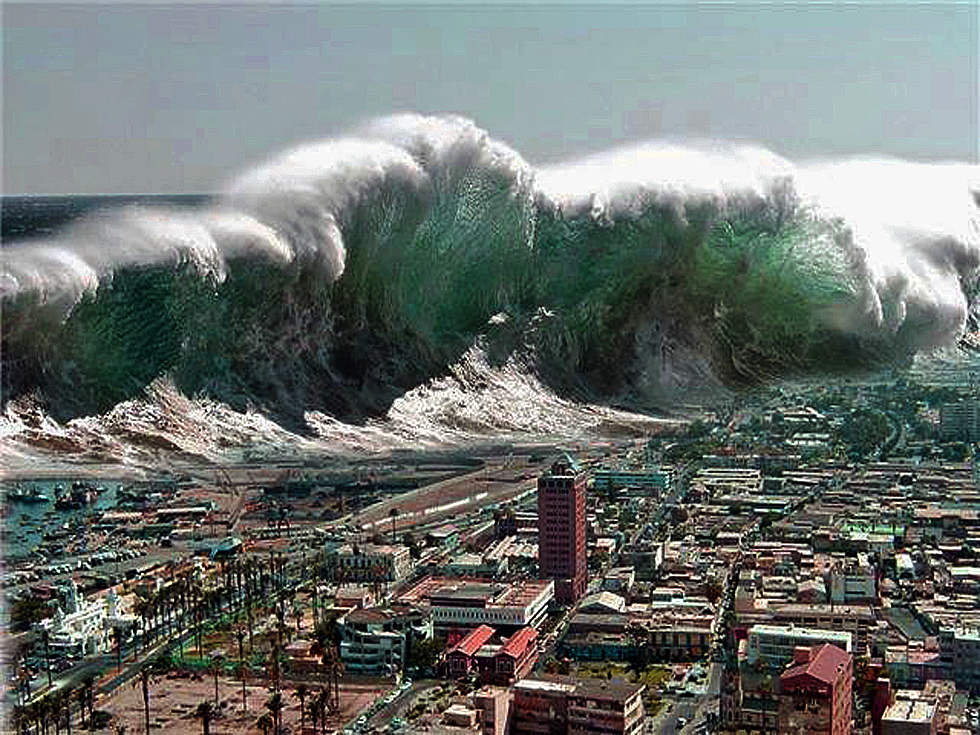

A new study is challenging a long-held theory that tsunamis form and acquire their energy mostly from vertical movement of the seafloor. The finding validates an approach developed by researchers that uses GPS technology to detect a tsunami’s size and strength for early warnings.
Sea level rising faster now than during 1990s, new study shows

Global mean sea level is rising 25 percent faster now than it did during the late 20th century largely due to increased melting of the Greenland Ice Sheet, a new study shows. Satellites first started measuring sea level rise in 1993. The new study revisits how well these measurements agree with independently observed changes in the various components contributing to sea level rise.
24 April 2017
Study finds pond expansion a significant factor in loss of Mississippi delta land
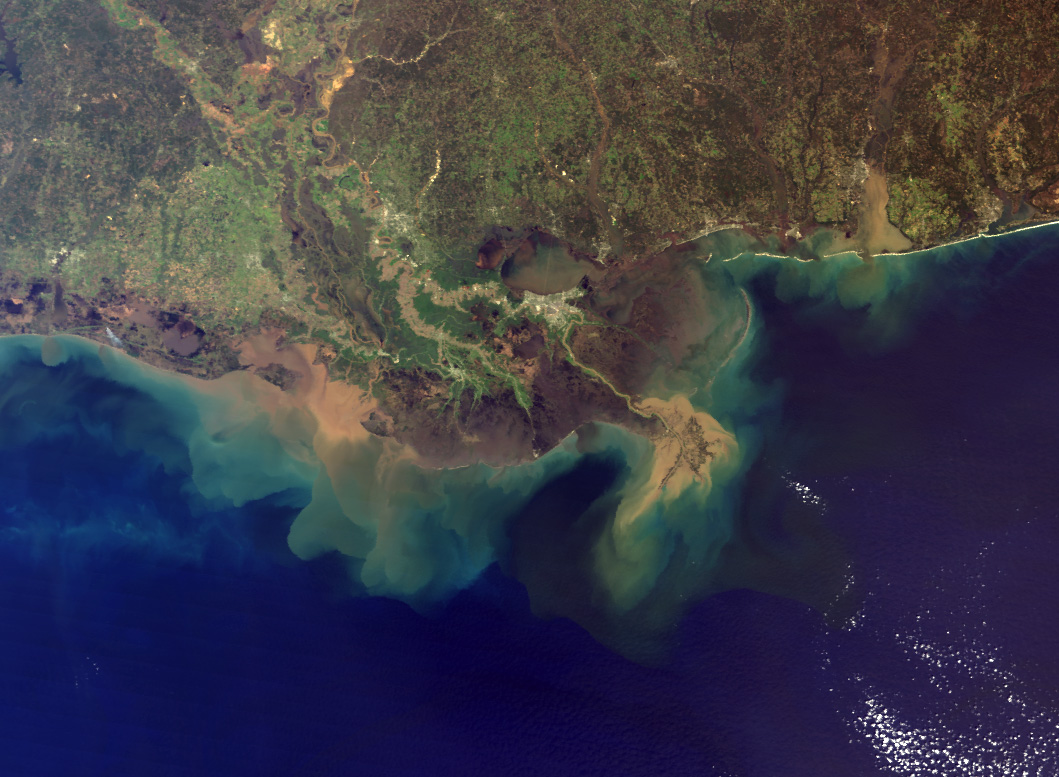

Wind-driven expansion of marsh ponds on the Mississippi River Delta is a significant factor in the loss of crucial land in the Delta region, according to new research. The study found 17 percent of land loss in the area resulted from pond expansion, much of it caused by waves that eroded away the edges of the pond.
18 April 2017
Mercury’s craters offer clues to planet’s contraction
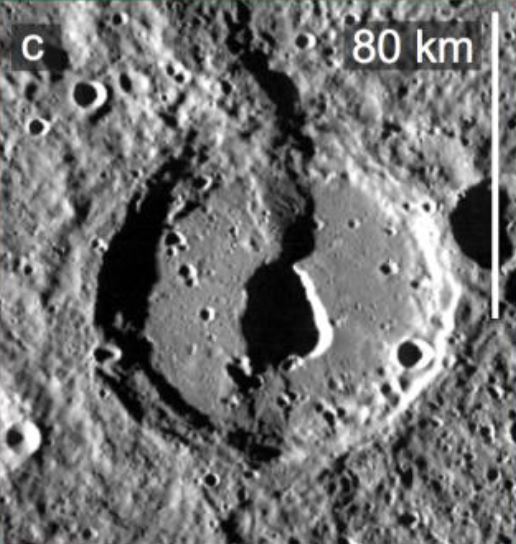

Craters serve as time-markers for the faults because they can be dated by how degraded they appear. The more degraded looking craters are older. Those that have sharper features are younger, and those with bright rays of debris radiating around them are youngest of all.
17 April 2017
Why can we see and hear meteors at the same time?

Light travels nearly a million times faster than sound. But for thousands of years, humans have reported hearing some meteors as they pass overhead, puzzling scientists for decades. Now, a new study puts forth a simple explanation for the phenomenon.
13 April 2017
Researchers unravel drivers of large iceberg movement
Researchers have succeeded in modeling how Antarctic icebergs drift through the Southern Ocean, and in identifying the physical factors behind their movement and their melting. Which factors are most important tends to depend on the size of the iceberg in question
12 April 2017
One-fifth of world’s population depends on food imports

Countries unable to feed their growing populations are increasingly importing food to meet demand, a new study finds. Nearly half of the world’s population lives in areas where imports compensate for food scarcity and one-fifth of the world now depends upon these imports to survive, according to the new study.
11 April 2017
Researchers find mushrooms may hold clues to effect of carbon dioxide on lawns
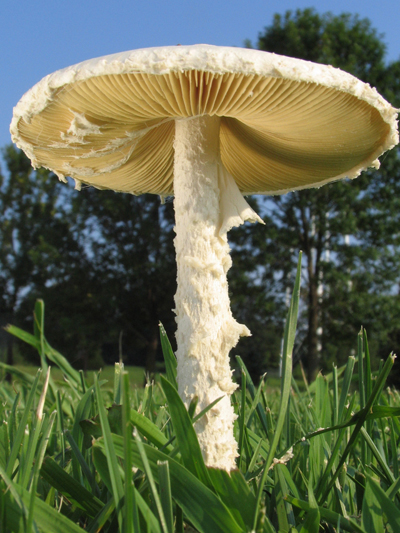

Researchers at the University of New Hampshire set out to determine how rising carbon dioxide concentrations and different climates may alter vegetation like forests, croplands, and 40 million acres of American lawns. They found that the clues may lie in an unexpected source, mushrooms.


 GeoSpace is a blog on Earth and space science, managed by AGU’s Public Information staff. The blog features posts by AGU writers and guest contributors on all sorts of relevant science topics, but with a focus on new research and geo and space sciences-related stories that are currently in the news.
GeoSpace is a blog on Earth and space science, managed by AGU’s Public Information staff. The blog features posts by AGU writers and guest contributors on all sorts of relevant science topics, but with a focus on new research and geo and space sciences-related stories that are currently in the news.