23 April 2020
Promising signs for Perseverance rover in its quest for past Martian life
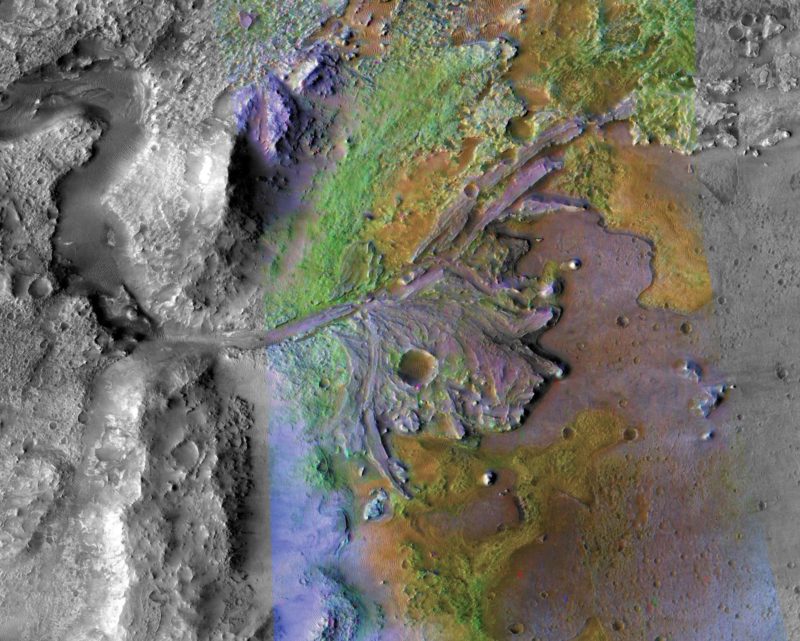

New research indicates river delta deposits within Mars’ Jezero crater – the destination of NASA’ Perseverance rover – formed over time scales that promoted habitability and enhanced preservation of evidence.
21 April 2020
South Asia faces increased double-threat of extreme heat, extreme pollution
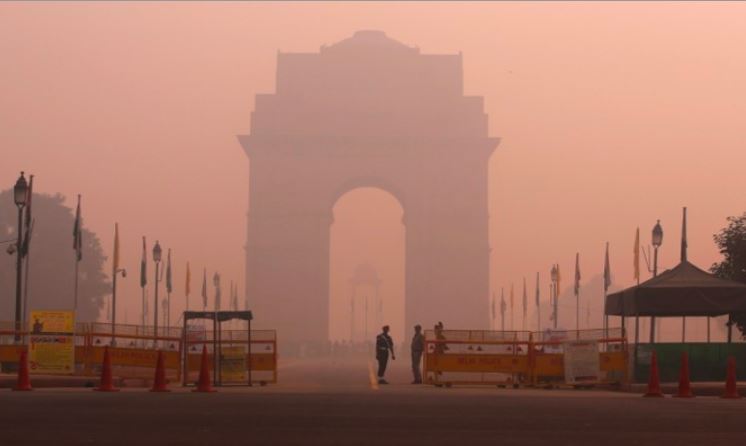

Extreme heat occurrences worldwide have increased in recent decades, and at the same time, many cities are facing severe air pollution problems, featuring episodes of high particulate matter pollution. This study provides an integrated assessment of human exposure to rare days of both extreme heat and high PM levels.
Continued carbon dioxide emissions will impair human cognition

Rising CO2 causes more than a climate crisis—it may directly harm our ability to think.
16 April 2020
Dust devils may roam hydrocarbon dunes on Saturn’s moon Titan
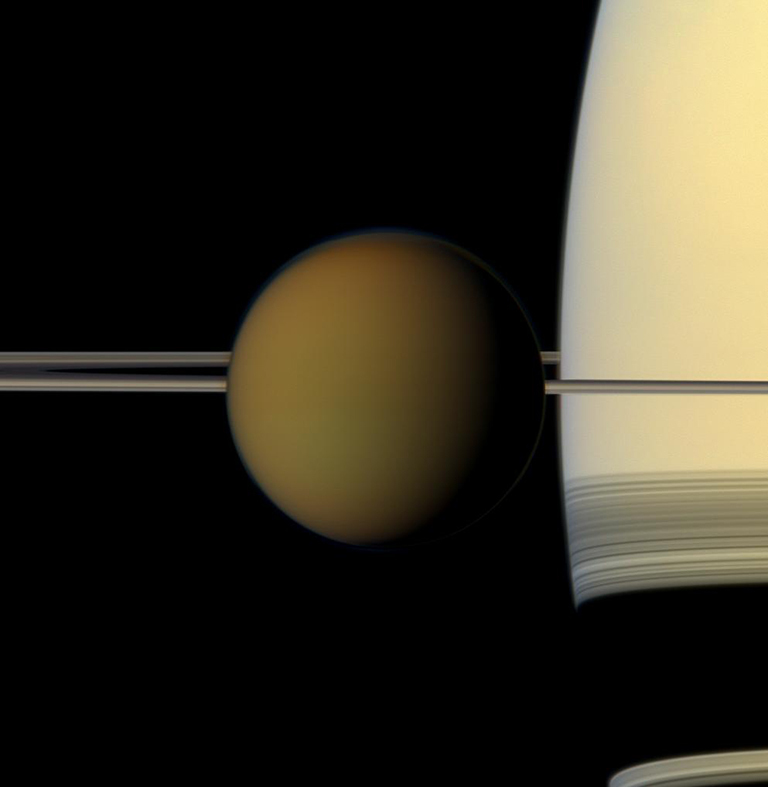
Smoggy, with a chance of dust devils: conditions at the surface of Saturn’s moon Titan may spawn convective whirlwinds By Liza Lester Meteorological conditions on Saturn’s large moon Titan, the strange, distant world that may be the most Earth-like in the solar system, appear conducive to the formation of dust devils, according to new research in AGU’s journal Geophysical Research Letters. If true, these dry whirlwinds may be primary movers …
9 April 2020
Greenland Ice Sheet meltwater can flow in winter, too
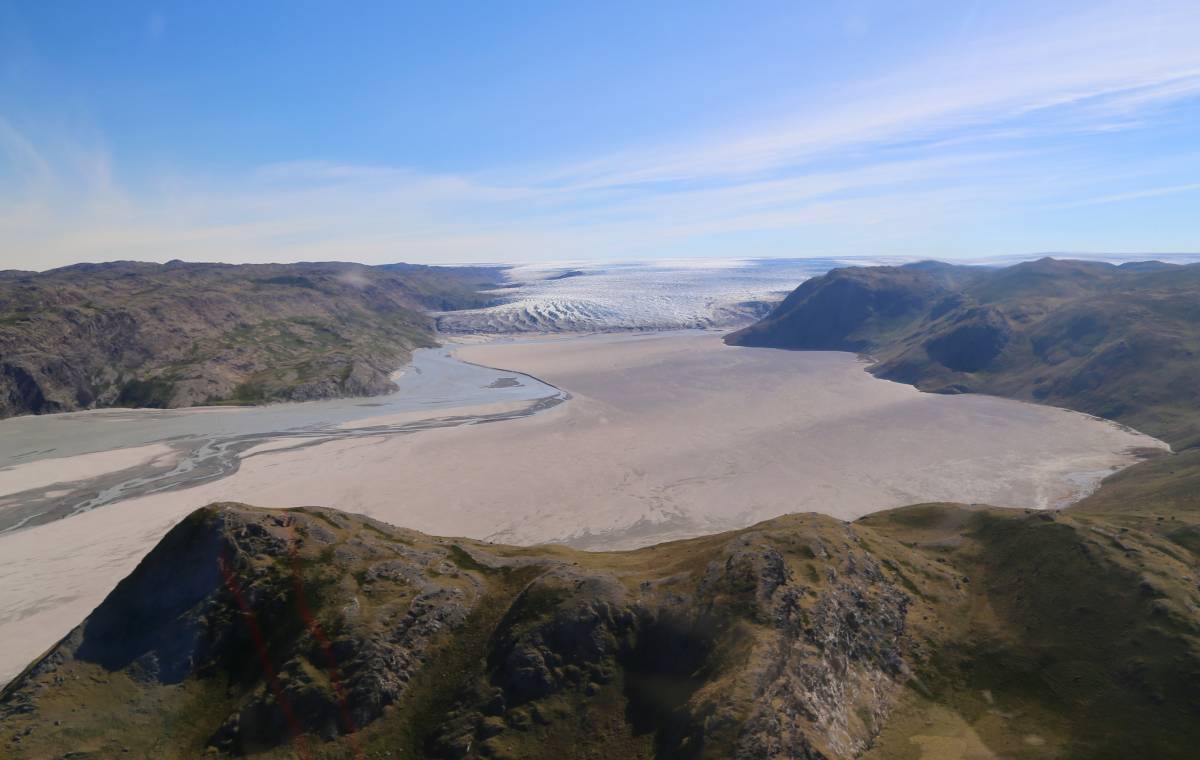

New findings published in Geophysical Research Letters underscore need for year-round investigations of Arctic hydrology.
8 April 2020
Shelf sediments, freshwater runoff from rivers brings more carbon, nutrients to North Pole
Freshwater runoff from rivers and continental shelf sediments are bringing significant quantities of carbon and trace elements into parts of the Arctic Ocean via the Transpolar Drift—a major surface current that moves water from Siberia across the North Pole to the North Atlantic Ocean.
7 April 2020
NASA study adds a pinch of salt to El Niño models
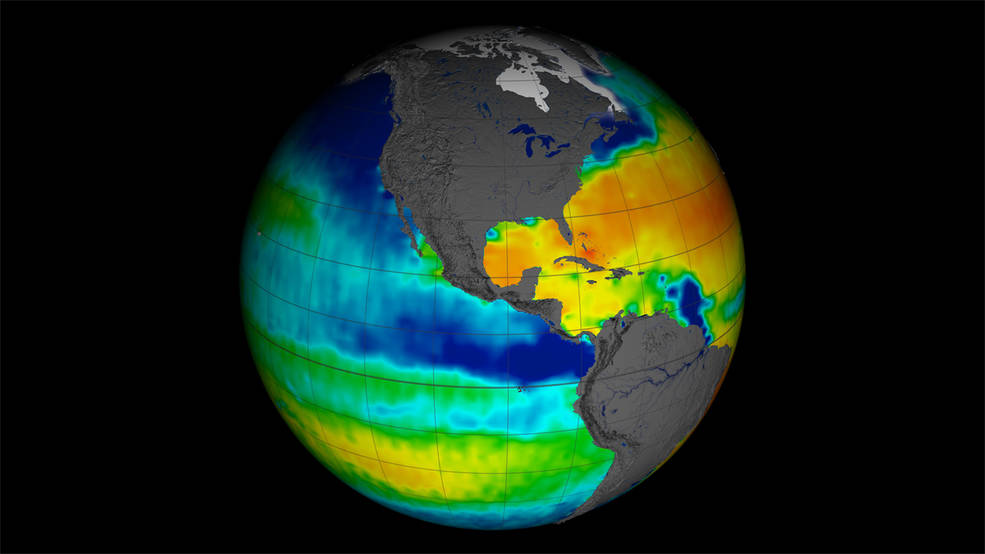
When modeling the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) ocean-climate cycle, adding satellite sea surface salinity — or saltiness — data significantly improves model accuracy, according to a new study. ENSO is an irregular cycle of warm and cold climate events called El Niño and La Niña. In normal years, strong easterly trade winds blow from the Americas toward southeast Asia, but in an El Niño year, those winds are reduced and sometimes even reversed. Warm water that was “piled up” in the western Pacific flows back toward the Americas, changing atmospheric pressure and moisture to produce droughts in Asia and more frequent storms and floods in the Americas. The reverse pattern is called a La Niña, in which the ocean in the eastern Pacific is cooler than normal.
Scientists propose explanation for night sky glow of STEVE
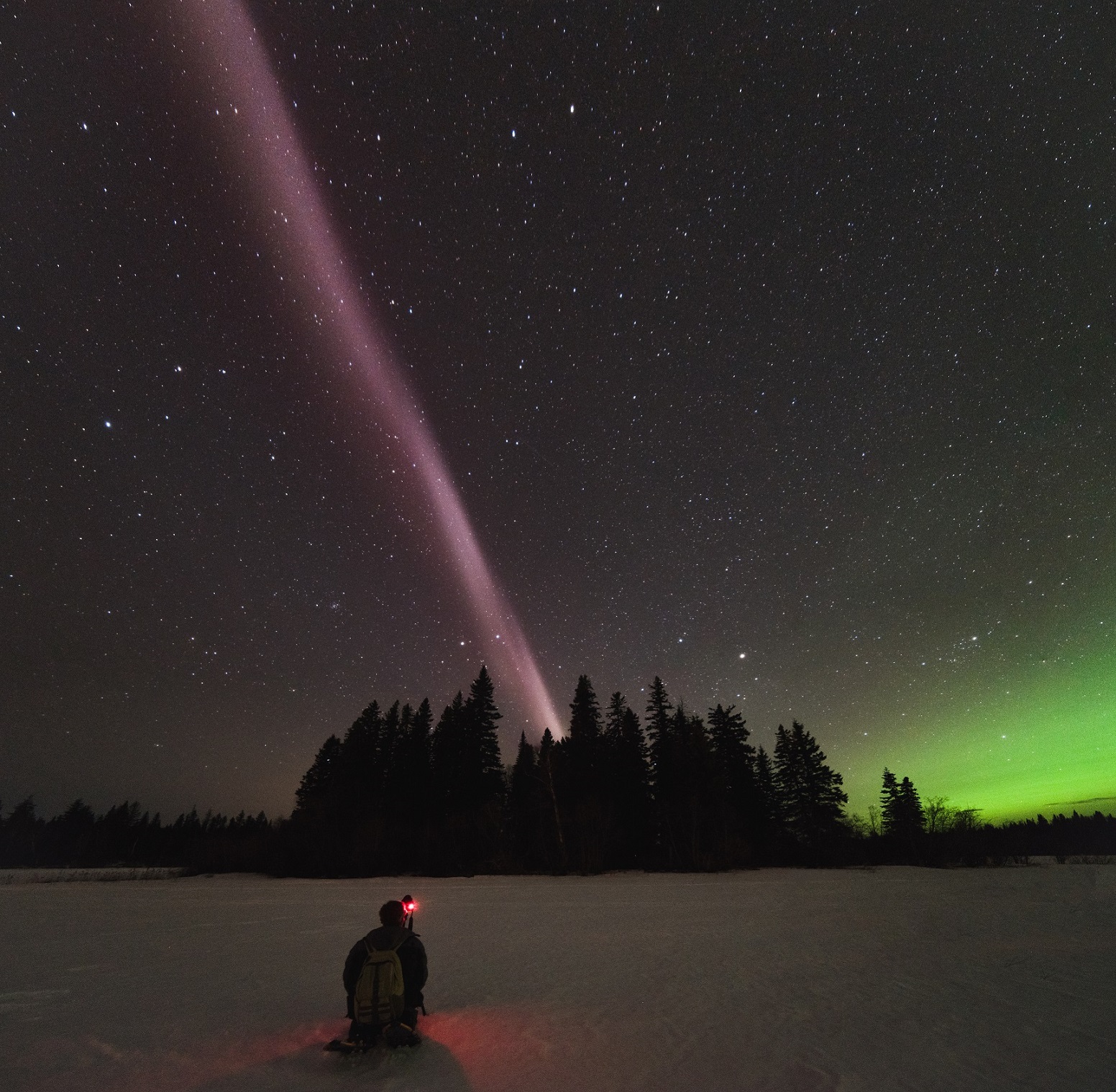

Researchers have just published a theory of what powers the celestial phenomenon known as STEVE, the aurora-like glow amateur sky-watchers brought to scientists’ attention in 2016. Scientists first thought STEVE was a new kind of aurora, but previous research shows its light is not produced the same way. Researchers are still unsure of what generates STEVE’s light, but a group of space physicists now suspect STEVE lights up when fast-flowing rivers of plasma jumpstart certain chemical reactions high in the atmosphere.
31 March 2020
Flooding Stunted 2019 Cropland Growing Season, Resulting in More Atmospheric CO2
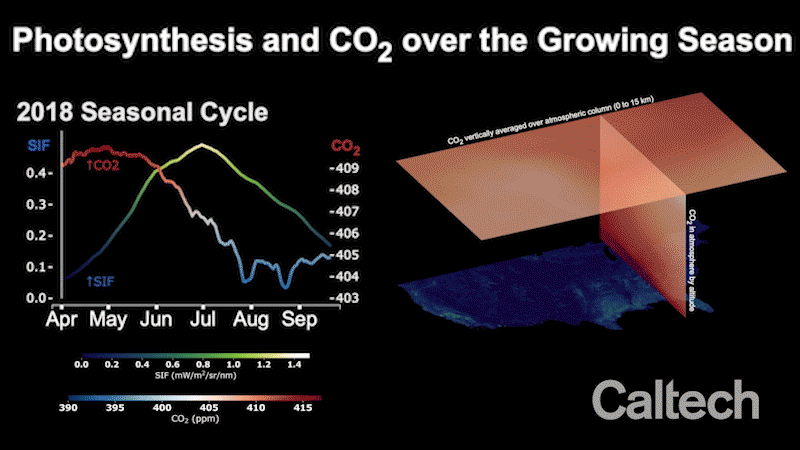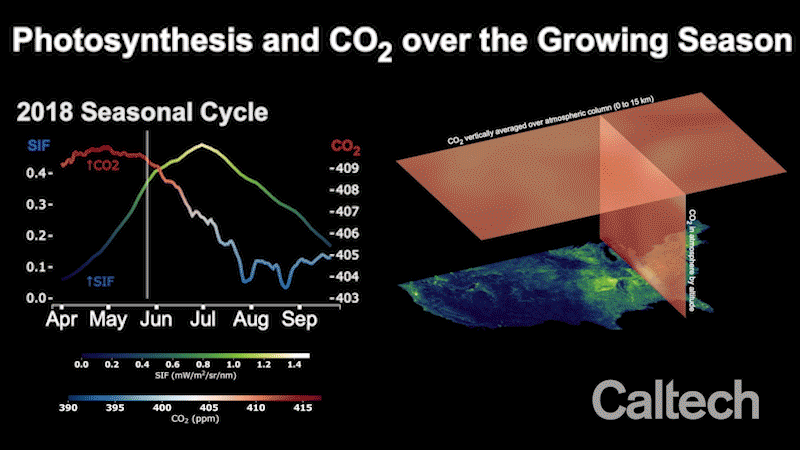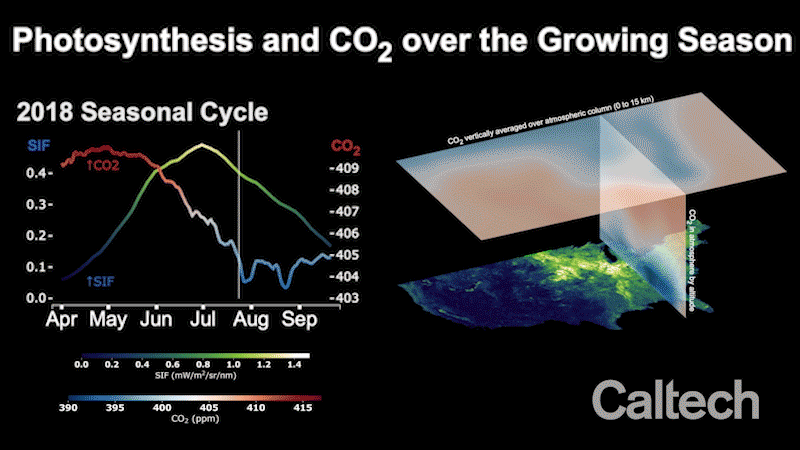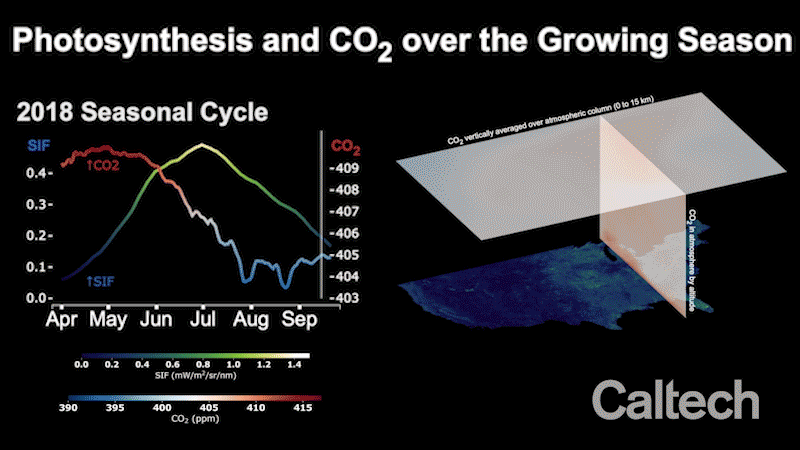
A new study determines the impact of the severe 2019 floods, and offers scientists a new tool for measuring regional-scale carbon dioxide absorption by plants.
19 March 2020
Darkness, not cold, likely responsible for dinosaur-killing extinction
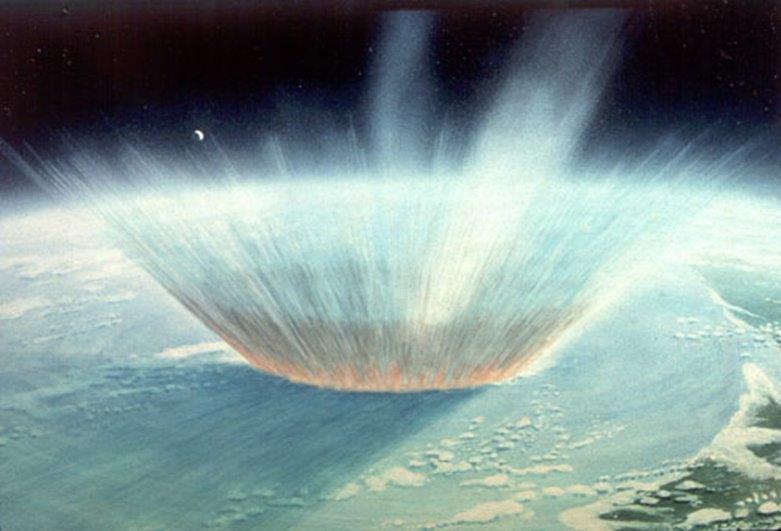

New research finds soot from global fires ignited by an asteroid impact could have blocked sunlight long enough to drive the mass extinction that killed most life on Earth, including the dinosaurs, 66 million years ago.










 GeoSpace is a blog on Earth and space science, managed by AGU’s Public Information staff. The blog features posts by AGU writers and guest contributors on all sorts of relevant science topics, but with a focus on new research and geo and space sciences-related stories that are currently in the news.
GeoSpace is a blog on Earth and space science, managed by AGU’s Public Information staff. The blog features posts by AGU writers and guest contributors on all sorts of relevant science topics, but with a focus on new research and geo and space sciences-related stories that are currently in the news.