24 April 2019
Uncovering polynya: new research unravels 43-year-old Antarctic mystery
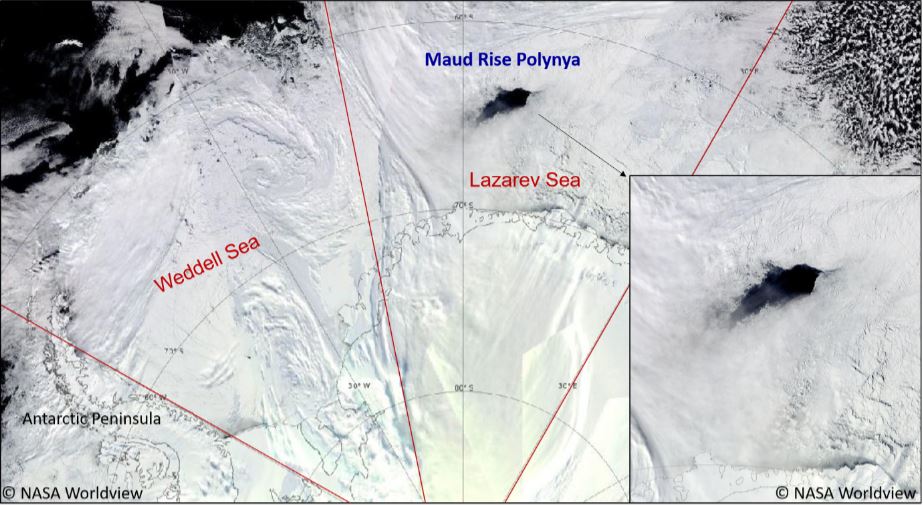
Researchers at NYU Abu Dhabi have discovered how the Maud-Rise Polynya that was initially spotted in Antarctica in 1974, reappeared in September 2017 at the same location.
23 April 2019
Aurora create speed bumps in space
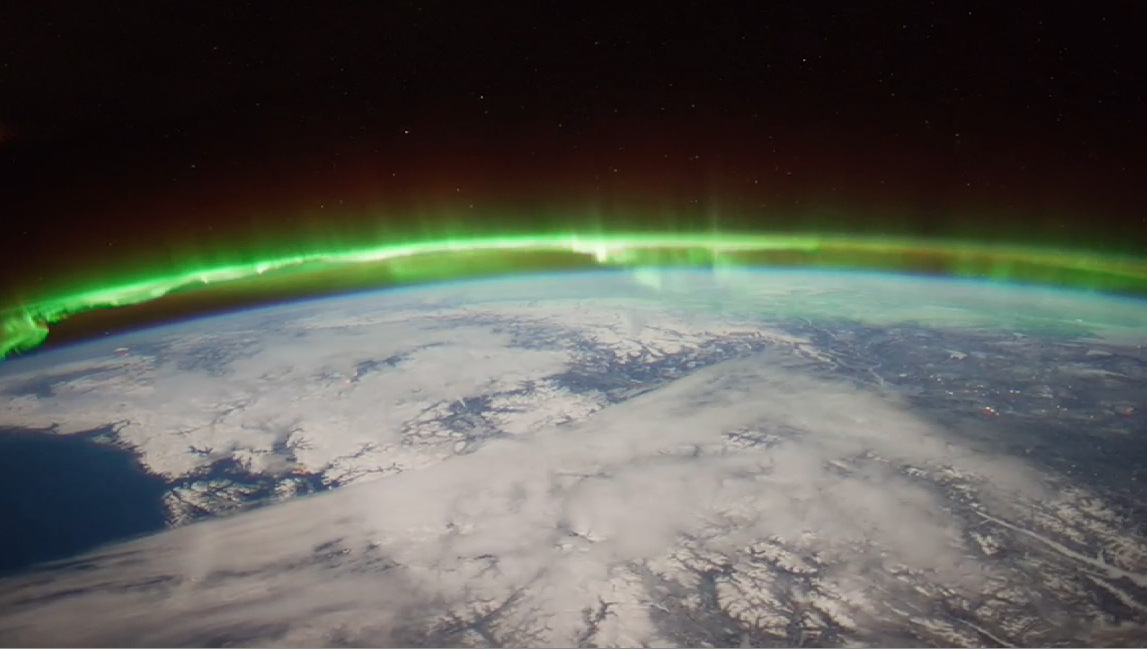

A new study finds a type of high-altitude aurora are responsible, at least in part, for moving pockets of air high into the atmosphere where they can cause drag on passing satellites.
22 April 2019
Microbes hitch a ride on high-flying dust
High-altitude dust may disperse bacterial and fungal pathogens for thousands of miles, seeding far-flung ecosystems and potentially impacting human health
New research explains why Hurricane Harvey intensified immediately before landfall

A new study explains the mechanism behind Hurricane Harvey’s unusual intensification off the Texas coast and how the finding could improve future hurricane forecasting.
18 April 2019
The Moon’s crust is really cracked

The bombardment of asteroids and meteoroids that pockmarked the Moon’s surface over the eons also created fractures reaching deep into the lunar crust, report researchers in a new study in AGU’s Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets.
16 April 2019
Dust toll in Africa exceeds deaths from HIV
New modeling indicates mineral dust from the Sahara is the biggest contributor to air pollution-related premature deaths on the African continent.
15 April 2019
Earliest life may have arisen in ponds, not oceans

Shallow bodies of water, on the order of 10 centimeters deep, could have held high concentrations of what many scientists believe to be a key ingredient for jump-starting life on Earth: nitrogen.
11 April 2019
Extended winter polar vortices chill Saturn’s strangely familiar moon, Titan
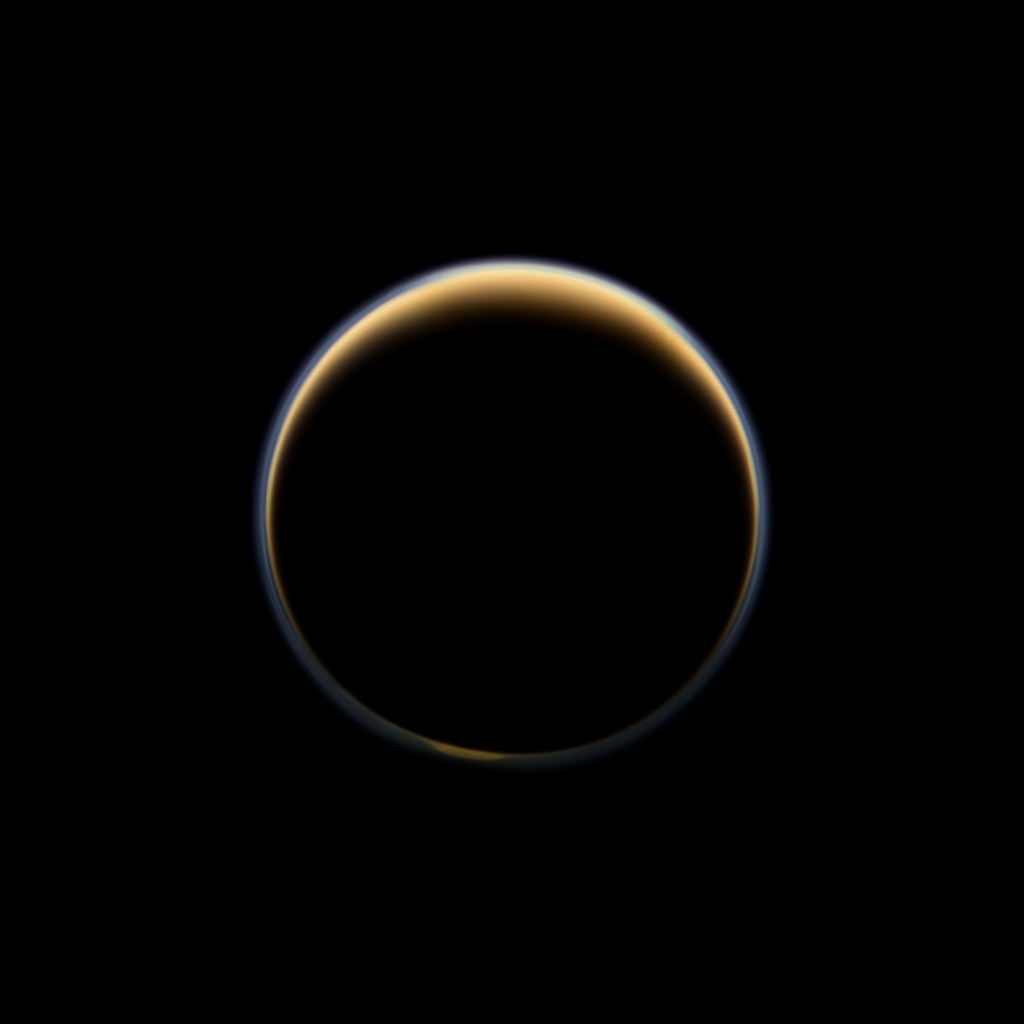

Saturn’s hazy moon Titan has a long-lived Earth-like winter polar vortex supercharged by the moon’s peculiar chemistry. A new study finds Titan’s northern hemisphere polar vortex sticks around past the moon’s summer solstice, into what would be late June on Earth, lasting three-quarters of a Titan year, or about 22 Earth years.
28 March 2019
California ‘browning’ more in the south during droughts

Like a climate chameleon, California turned brown during the 2012–16 drought, as vegetation dried or died off. But the change wasn’t uniform. Large areas of the northern part of the state were not severely affected, while Southern California became much browner than usual…
25 March 2019
Laser Blasts Show Asteroid Bombardment, Hydrogen Make Great Recipe for Life on Mars

A new study reveals asteroid impacts on ancient Mars could have produced key ingredients for life if the Martian atmosphere was rich in hydrogen. An early hydrogen-rich atmosphere on Mars could also explain how the planet remained habitable after its atmosphere thinned.










 GeoSpace is a blog on Earth and space science, managed by AGU’s Public Information staff. The blog features posts by AGU writers and guest contributors on all sorts of relevant science topics, but with a focus on new research and geo and space sciences-related stories that are currently in the news.
GeoSpace is a blog on Earth and space science, managed by AGU’s Public Information staff. The blog features posts by AGU writers and guest contributors on all sorts of relevant science topics, but with a focus on new research and geo and space sciences-related stories that are currently in the news.