April 7, 2021
Bonar Glacier Retreat, New Zealand
Posted by Mauri Pelto
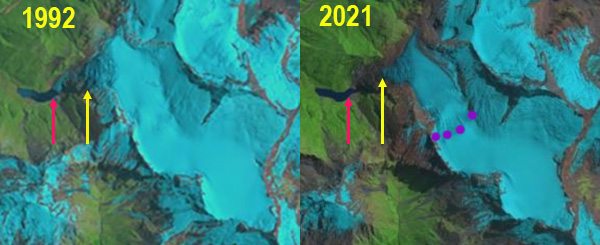
Bonar Glacier in 1992 and 2021 Landsat image. Red arrow is the 1992 reconstituted terminus location, yellow arrow the 2021 terminus location and purple dots the snowline.
Bonar Glacier is on the west flank of Mount Aspiring flowing north from Mount before turning sharply west and descending towards a lake and draining into the Waipara River. The NIWA glacier monitoring program noted that 30 per cent of New Zealand’s ice that was existed in the late 1970s has been lost in the past 40 years as snowlines have been rising. The retreat has been driven by a series of increasingly warm summers (NIWA, 2019). Bonar Glacier is one of the six largest west side glaciers in the NZ Alps and has no significant debris cover (Baumman et al 2021). Here we examine Landsat imagery from 1992-2021 to identify changes.
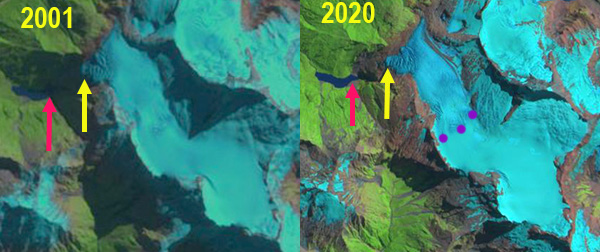
In 1992 the glacier descends west down the steep slope to its terminus at 1150 m avlanching down the steep slope to a reconstituted glacier at the head of a 1 km long proglacial lake at ~550 m. In 2001 there is no reconstituted glacier at the lake, the terminus is at ~1200 m in elevation. By 2020 the glacier terminus has receded to ~1250 m, the snowline is at 1900 m above the first icefall in early March. In 2021 the glacier has retreated 200 m, with its overall length being reduced by 3% since 1992. The snowline in 2021 is again at the top of the 1900 m icefall.
The retreat is more limited than at either Volta Glacier which is on the east side of Mount Aspiring, or at Snow White Glacier to the southwest. The mean elevation of glaciers in New Zealand is 1950 m (Baumman et al 2021). The mean elevation of Bonar Glacier is 2075-2090 m, which has enabled the glacier to endure recent warming better.
Bonar Glacier in aerial image from 2020, with red arrow indicating 1992 terminus location, note heavily crevassed areas on the east side draining from 2500 m on the slopes of Mount Aspiring and at the three icefalls areas on the main glacier.
Bonar Glacier topographic map, blue arrows indicate glacier flow. Icefalls at 2000 m, 1800 m and from 1600 m to the terminus at 1300 m.
Bonar Glacier in 2001 and 2020 Landsat image. Red arrow is the 1992 reconstituted terminus location, yellow arrow the 2021 terminus location and purple dots the snowline.




 Dean of Academic Affairs at Nichols College and Professor of Environmental Science at Nichols College in Massachusetts since 1989. Glaciologist directing the North Cascade Glacier Climate Project since 1984. This project monitors the mass balance and behavior of more glaciers than any other in North America.
Dean of Academic Affairs at Nichols College and Professor of Environmental Science at Nichols College in Massachusetts since 1989. Glaciologist directing the North Cascade Glacier Climate Project since 1984. This project monitors the mass balance and behavior of more glaciers than any other in North America.