April 3, 2018
Warsaw Icefield, King George Is., Antarctica Retreating from Shoreline
Posted by Mauri Pelto
Warsaw Icefield, King George Island, Antarctica glacier retreat and nunatak expansion in 1989, 2001 and 2018 Landsat images. E=Ecology Glacier, B=Baranowski Glacier, W=Windy Glacier, 1989 terminus locations indicated by red arrows. Point A & B are nunataks.
The Arctowski Polish Research Station is located on a relatively large ice-free oasis northeast of the Warsaw Icefield on King George Island, Antarctica. The station is on Admiralty Bay where Ecological monitoring has been conducted since the late 1970’s in order to determine the size and condition of populations of seabirds and pinnipeds. The ocean bottom has had over 800 distinct benthic species identified. A long term study of a chinstrap penguin colony on King George Islands during the last 30 years indicates the size of the breeding populations has decreased by 84% probably due to limitations of the marine food web (Korczak-Abshire et al 2012). The outlet glaciers of Warsaw Icefield experienced significant retreat and mass loss (Petlicki et al, 2017). Here we examine Landsat images from 1989 to 2017 to illustrate the changes. The Warsaw Icefield extends from 400 m to sea level.
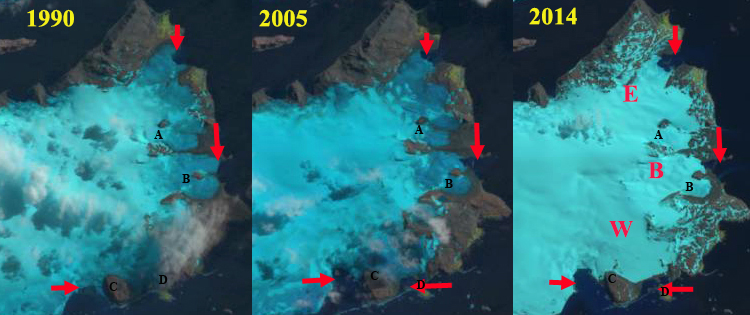
In 1989 Baranowski and Windy Glacier terminate on the coastline lacking any significant embayment. Ecology Glacier has a wide front in a shallow embayment. Nunataks A and B are amidst the icefield. In 1990 the snowline is at 200 m with nunatak A and B in the ablation zone. In 2001 nunatak A and B are still surrounded by ice. Windy Glacier and Baranowski Glacier have retreated with embayments forming. The embayments are separated from ocean by a coastal strip of land. An embayment has also opened to the west of Windy Glacier and Point C due to glacier retreat. In 2005 the snowline is at 250 m. Baranowski glacier retreat has led to Nunatak B reaching the margin of the glacier, the embayment expanding on the north side of the margin. In 2014 Ecology Glacier has retreated opening the embayment. In 2018 Ecology Glacier has retreated 600 m since 1989 exposing several small new islands in this protected embayment. the Tidewater front is quite limited in 2018. Nunatak A is within 400 m of the edge of the icefield, whereas in 1989 the nunatak was 1.2 km from the margin. The 1989-2018 500 m retreat of Baranowski Glacier has led to the development of a dominantly land based terminus. Windy Glacier has retreated 400 m since 1989 and is now land terminating. The glacier to the west of Windy Glacier and Point C has opened a 0.5 square kilometers embayment. The retreat of Warsaw Icefield is similar to that of Endurance Glacier, Elephant Island. Petlicki et al,( 2017) indicate mass balance has not been as negative from 2012-2016 which should slow retreat. The new embayments offer potential new locations for penguins that Arctowski scientists will monitor.
Warsaw Icefield, King George Island, Antarctica glacier retreat and nunatak expansion in 1990, 2005 and 2014 Landsat images. E=Ecology Glacier, B=Baranowski Glacier, W=Windy Glacier. Point A & B are nunataks in 1989.
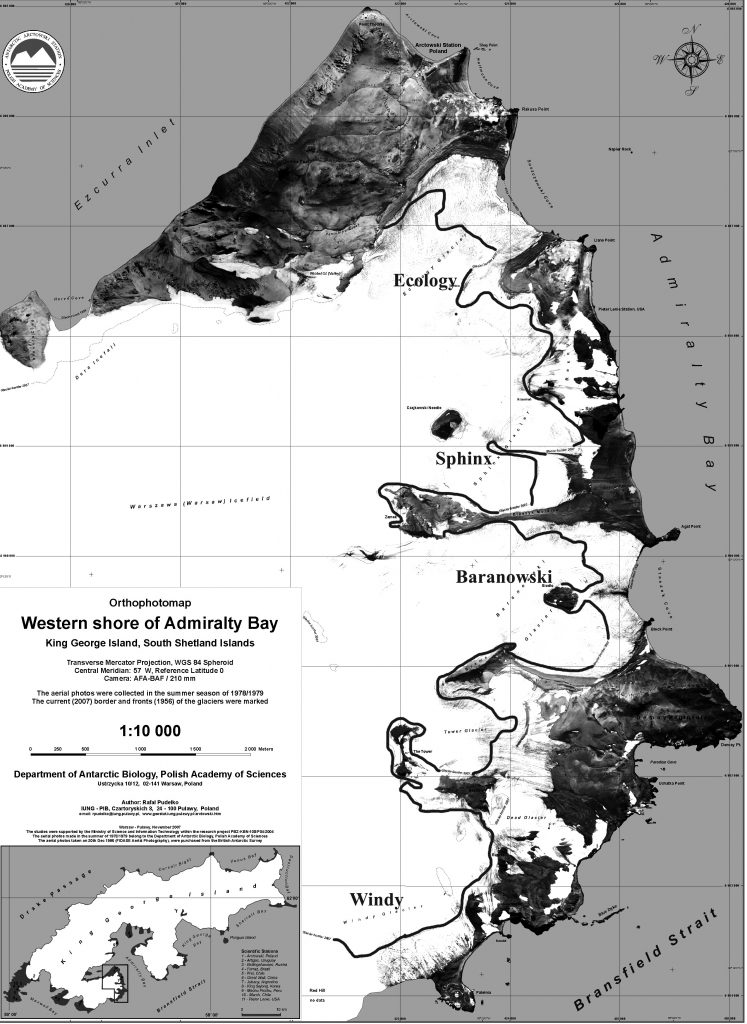
Map from the Arctowski Research Station in 2007 indicating glacier changes from 1978 mapped margins to 2007 dark line margin. This dark line has been annotated to be visible for this post.



 Dean of Academic Affairs at Nichols College and Professor of Environmental Science at Nichols College in Massachusetts since 1989. Glaciologist directing the North Cascade Glacier Climate Project since 1984. This project monitors the mass balance and behavior of more glaciers than any other in North America.
Dean of Academic Affairs at Nichols College and Professor of Environmental Science at Nichols College in Massachusetts since 1989. Glaciologist directing the North Cascade Glacier Climate Project since 1984. This project monitors the mass balance and behavior of more glaciers than any other in North America.