April 14, 2013
Twitcher Glacier Accelerated Retreat, South Georgia island
Posted by Mauri Pelto
Twitcher Glacier is the next glacier south of Herz Glacier on the east coast of South Georgia. Until 1989 the glacier ended at the tip of a peninsula, the ensuing retreat has led to the opening of a new fjord. Twitcher Glacier was 10 km long and had a 2 km wide calving front in 2009. The terminus change of this tidewater glacier was completed by the British Antarctic Survey for the 1960-2007 period. The glacier retreated 1.5 km between 1960 and 2007, with have of the retreat occurring after 1992. (Gordon et al, 2008). The map below indicates the slow retreat from 1960-1988 and a more rapid retreat since.
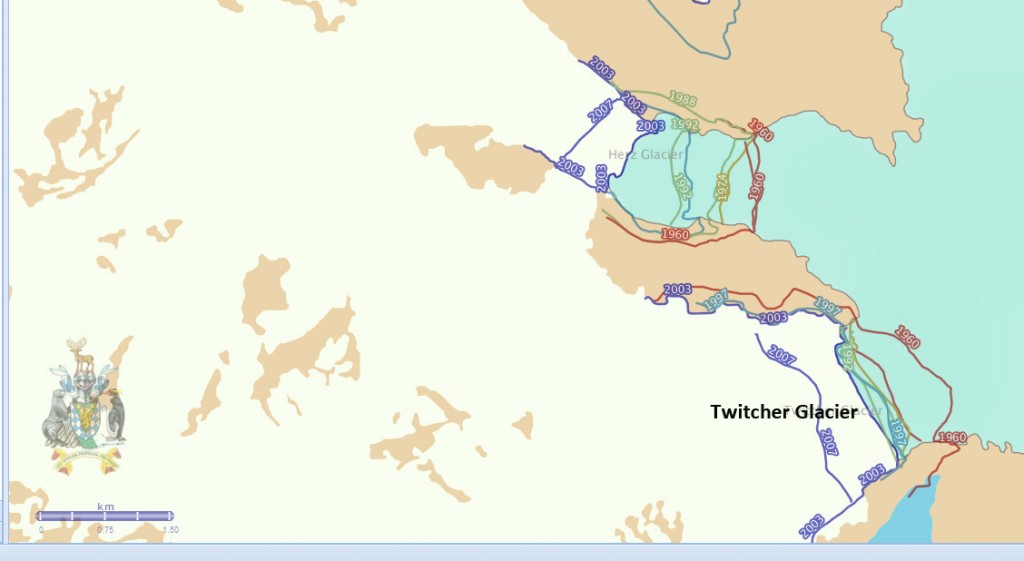
BAS Map of glacier front change
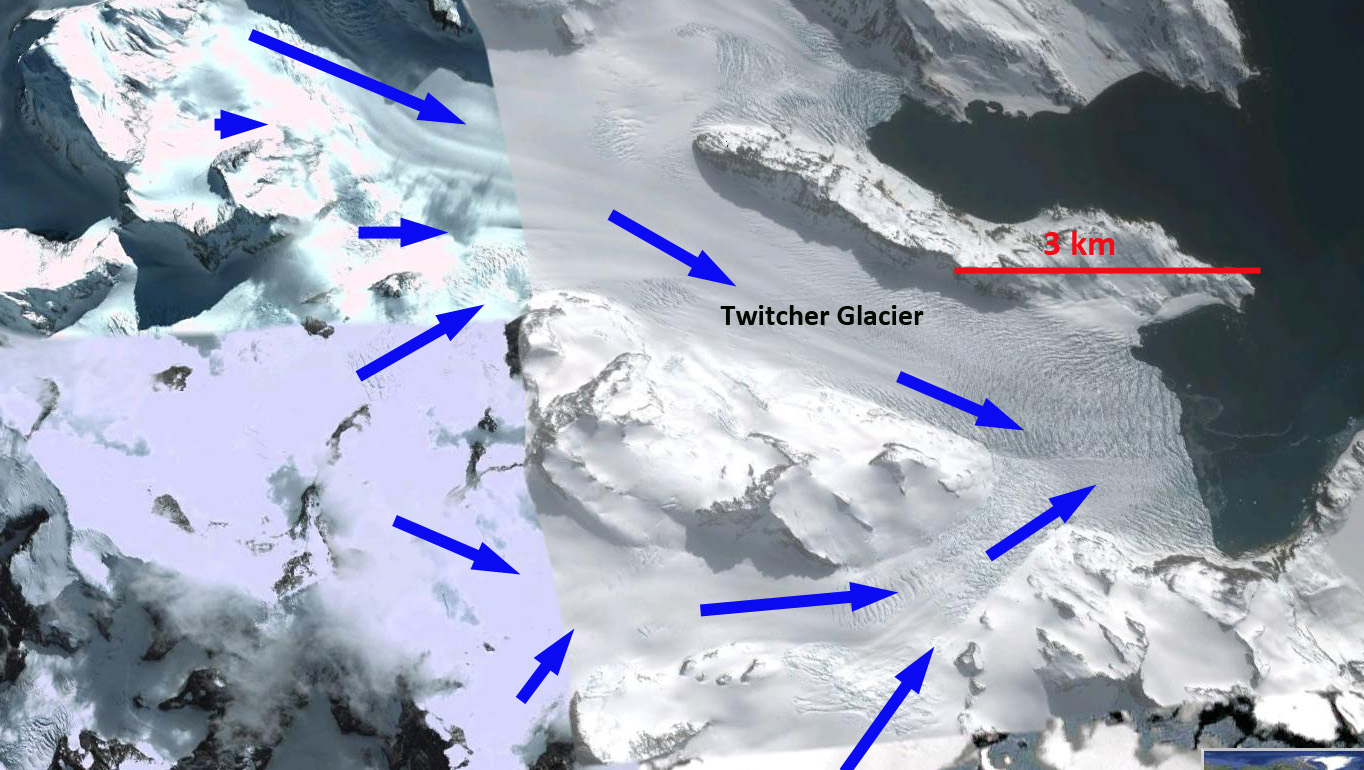
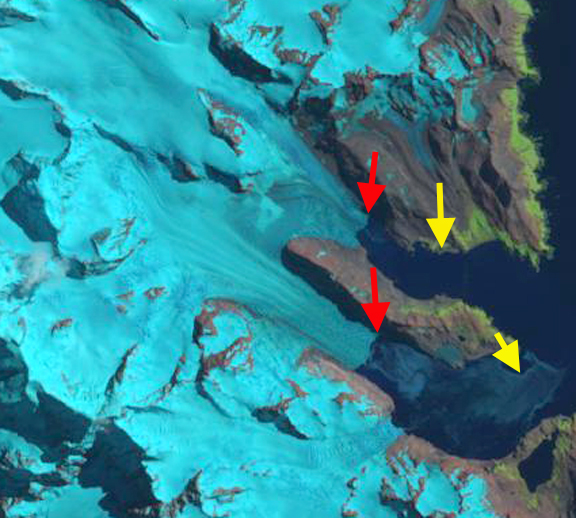
In 1989 this glacier terminated approximately at the end of a peninsula separating the two glaciers. Here we examine Landsat imagery from 1989, 2000, 2009 and 2015 to identify the rate retreat. The 1989 terminus position is indicated with a yellow arrow and the 2009 terminus position with a red arrow. The retreat is 1.2 km during this period from 18989-2009. From 2009 to 2015 retreat accelerated with a further 1.7 km retreat to the red arrow in the 2015 imagery. The last image is a closeup in Google Earth from 2010 note the significant crevassing which is indicative of rapid flow. The terminus is currently quickly retreating to the next peninsula where the terminus will separate into two parts. The southern tributary already is partly exposed to calving into the fjord. The rapid retreat here is similar to that of Neumayer Glacier or Ross Hindle Glacier.

1989 Landsat image
2000 Landsat Image
2009 Landsat Image

Google Earth image of crevassed front




 Dean of Academic Affairs at Nichols College and Professor of Environmental Science at Nichols College in Massachusetts since 1989. Glaciologist directing the North Cascade Glacier Climate Project since 1984. This project monitors the mass balance and behavior of more glaciers than any other in North America.
Dean of Academic Affairs at Nichols College and Professor of Environmental Science at Nichols College in Massachusetts since 1989. Glaciologist directing the North Cascade Glacier Climate Project since 1984. This project monitors the mass balance and behavior of more glaciers than any other in North America.