18 October 2016
Soil moisture, snowpack data could help predict ‘flash droughts’
Posted by Lauren Lipuma
Severe 2012 drought could have been predicted months in advance
By Laura Snider

New research shows flash droughts, such as the one that hit Wisconsin in 2012, can be predicted several months in advance.
Credit: Samuel Zipper.
New research suggests “flash droughts” — like the one that unexpectedly gripped the Southern Rockies and Midwest in the summer of 2012 — could be predicted months in advance using soil moisture and snowpack data.
Researchers analyzed the conditions leading up to the 2012 drought, which ultimately caused $30 billion in economic losses, looking for any warning signs that a drought was on the way. In a new study published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, a journal of the American Geophysical Union, the scientists find observations of snowmelt and soil moisture could have predicted the ensuing drought up to four months in advance.
“The 2012 drought over the Midwest was one of the most severe and extensive U.S. droughts since the 1930s Dust Bowl, but it was also extremely challenging to predict,” said Debasish PaiMazumder, an atmospheric scientist at the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) in Boulder, Colorado and lead author of the study. “This study demonstrated the potential to improve seasonal drought outlooks in the future, giving farmers, water planners, and others more time to prepare.”
Seasonal drought forecasts issued in May 2012 for the upcoming summer did not foresee a drought forming in the country’s midsection. But by the end of August, a drought that had started in the Southern Rockies had spread across the Midwest, parching Oklahoma, Kansas, Nebraska, and Missouri.
These flash droughts — which form and intensify rapidly — can catch forecasters off guard because they are not preceded by any large-scale climate patterns that could act as a warning signal. For example, one contributor to the recent California drought was a persistent high-pressure system parked off the west coast of Canada that deflected storms away from the state. Because forecasters could identify the high-pressure system, they could also accurately predict fewer storms and a worsening of the drought.
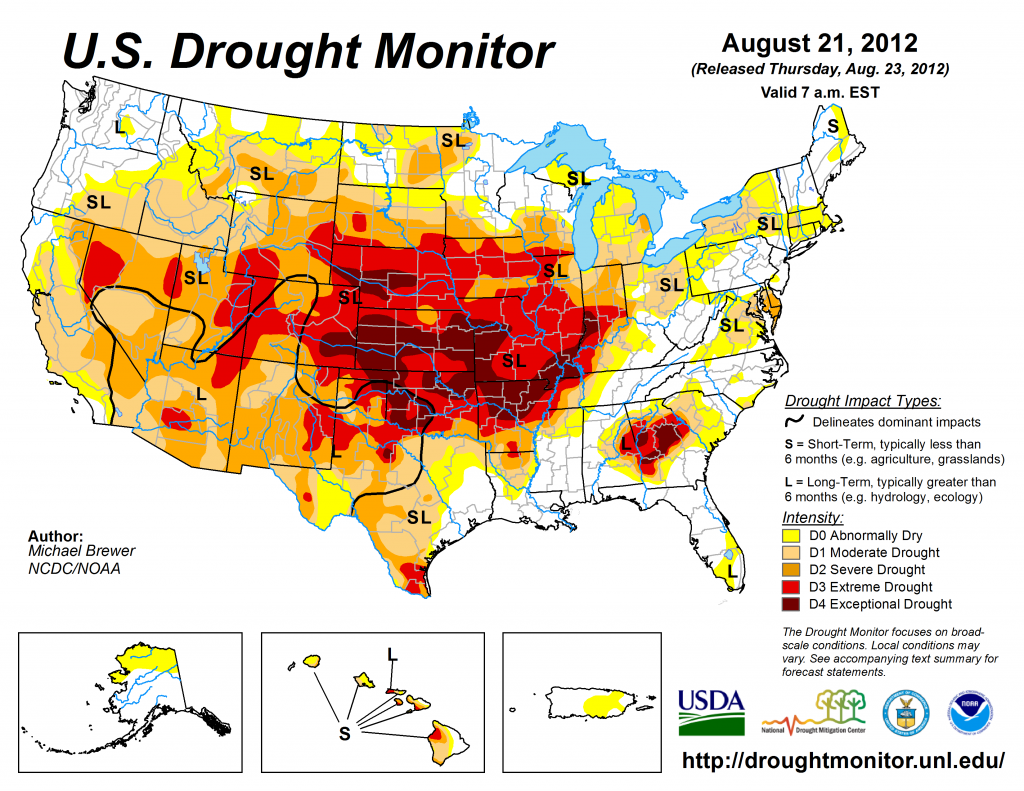
The official U.S. Drought Monitor issued on Aug. 21, 2012. The map shows the exceptionally severe drought across the middle of the country. Just three months before, drought forecasts failed to predict that a drought was on the way.
Credit: National Drought Mitigation Center.
Previous research has shown that looking at soil moisture alone could improve the lead-time of drought predictions by one to two months. PaiMazumder and NCAR colleague James Done were interested in whether they could extend this further by adding snowpack into the equation.
“Advance knowledge of a drought even a month or two ahead of time can greatly minimize the effects on society,” said Anjuli Bamzai, program director in NSF’s Division of Atmospheric and Geospace Sciences, which funded the research. “This study highlights the role of snowpack and soil moisture conditions in predicting the sudden onset of drought.”
To explore the physical connections among snowpack, soil moisture, and drought, the researchers analyzed data collected between 1980-2012. To supplement those observations, they also explored the physical connections in a new NCAR-based community Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model dataset comprising 24 simulations of the period 1990-2000 and 2012. Because each simulation was run with small tweaks to the way the model represents atmospheric physics, the result was a broad look at different climate scenarios that could have plausibly unfolded during the study period.
“The model helped us get a handle on how robust the relationships between snowpack, soil moisture, and drought are,” Done said. “The stronger the relationship, the better a predictor is.”
While observations of snowpack and soil moisture could have helped predict the 2012 drought, the method does not replace other drought prediction measures that identify large-scale phenomena that frequently lead to drought conditions.
“This is another ingredient that could be used when making seasonal drought forecasts,” Done said. “But it’s not the only ingredient, and for many droughts that are tied to large-scale precursors, it may not be the most important one.”
—Laura Snider is a Senior Science Writer and Public Information Officer at the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR). This post originally appeared as a press release on the NCAR website.


 GeoSpace is a blog on Earth and space science, managed by AGU’s Public Information staff. The blog features posts by AGU writers and guest contributors on all sorts of relevant science topics, but with a focus on new research and geo and space sciences-related stories that are currently in the news.
GeoSpace is a blog on Earth and space science, managed by AGU’s Public Information staff. The blog features posts by AGU writers and guest contributors on all sorts of relevant science topics, but with a focus on new research and geo and space sciences-related stories that are currently in the news.