April 7, 2015
31 years of observations on Retreating Columbia Glacier, Washington
Posted by Mauri Pelto
For the last 31 years the first week of August has found me on the Columbia Glacier in the North Cascades of Washington. Annual pictures of the changing conditions from 1984 to 2014 are illustrated in the time lapse video below. This is the lowest elevation large glacier in the North Cascades. Columbia Glacier occupies a deep cirque above Blanca Lake and ranging in altitude from 1400 meters to 1700 meters. Kyes, Monte Cristo and Columbia Peak surround the glacier with summits 700 meters above the glacier. The glacier is the beneficiary of heavy orographic lifting over the surrounding peaks, and heavy avalanching off the same peaks. This winter has been the lowest year for snowpack in the North Cascades in the 32 years we have worked here. Below is a comparison from August 1, 2011 with Blanca Lake below the glacier still frozen and a beautiful scene on April 4, 2015 with the lake not frozen taken by Karen K. Wang. The winter in the region was unusually warm, but not as dry as in California; however, in the snowmelt and glacier fed river basins summer runoff will be low this year.

Blanca Lake Aug. 1, 2011 on left, and April 4, 2015 on right (Karen K. Wang, www.karenkwang.com)
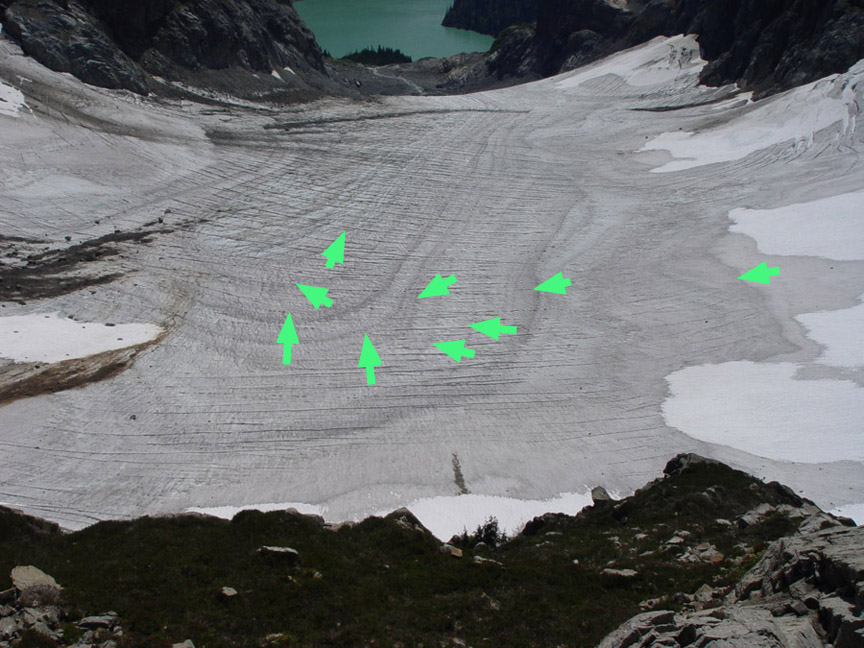
Over the last 31 years the annual mass balance measurements indicate the glacier has lost 14 meters of thickness. Given the average thickness of the glacier of close to 75 meters in 1984 this represents a 20% loss in glacier volume. During the same period the glacier has retreated 135 meters, 8% of its length. Most of the loss of volume of this glacier has been through thinning not retreat. To survive a glacier must have a persistent and consistent accumulation zone (Pelto, 2010). On Columbia Glacier in 1998, 2001, 2003, 2004, 2005, 2009 and 2013 limited snowpack was retained, resulting in thinning even on upper part of the glacier. This thinning of the upper glacier indicates the lack of a persistent accumulation zone such as in 2005, note the exposed annual ice and firn layers green arrows, this indicates the lack of retained accumulation in recent years. This indicates the glacier is in disequilibrium and cannot survive. Mapping of the glacier from the terminus to the head indicates a similar thinning along the entire length of the glacier. The overall mass balance loss parallels that of the globe and other North Cascade glaciers in the last three decades.
2005 Accumulation zone of Columbia Glacier
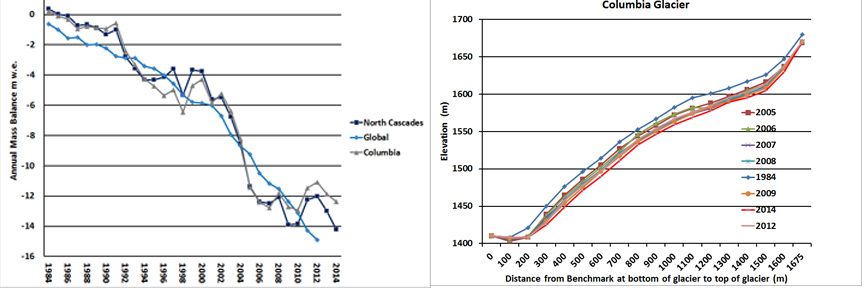
On left cumulative mass balance of Columbia Glacier compared to the WGMS global record and other North Cascade glaciers. On right change in surface elevation along the glacier from terminus to head indicating a 14-15 m thinning on average.
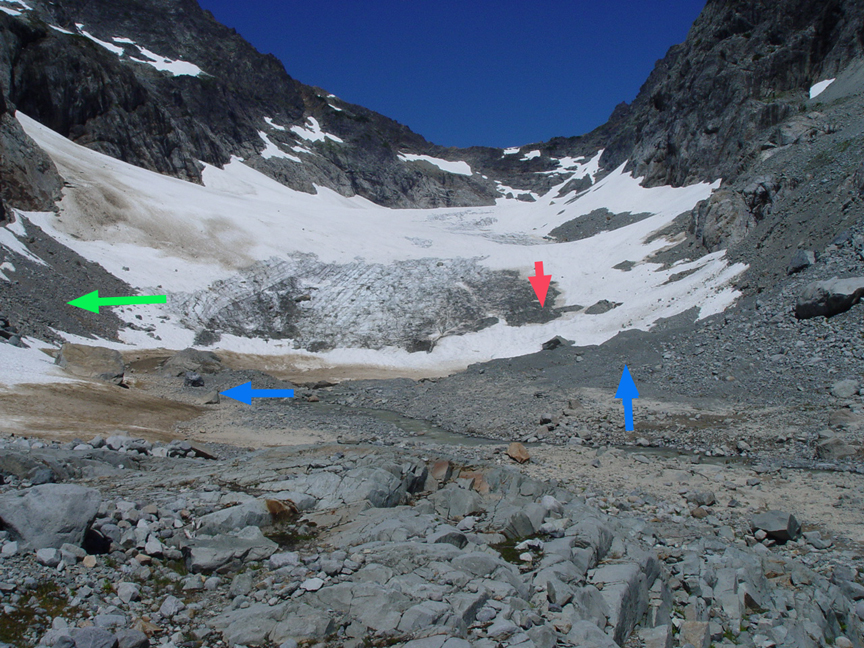
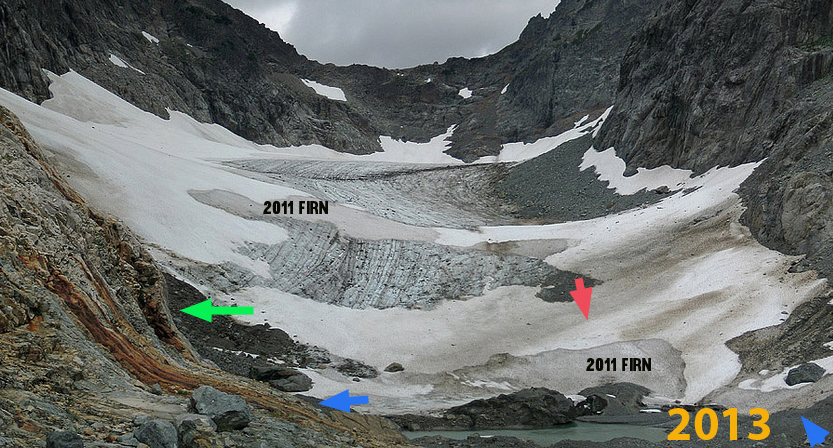
A comparison of images from 1986, 2007 and 2013 photograph provide a view of glacier change at the terminus. The blue arrows indicate moraines that the glacier was in contact with in 1986, and now are 100 meters from the glacier. The green arrow indicates the glacier active ice margin in 1986 and again that same location in 2007 now well off the glacier. The red arrow indicates the same location in terms of GPS measurements, this had been in the midst of the glacier near the top of the first main slope in 1986. In 2007 this location is at the edge of the glacier in a swale. The changes are more pronounced in 2013 as the terminus slope continues to decrease. The low snowpack in 2015 on the glacier in March, 2-3 m versus 6-8 m, will lead to considerable changes in the terminus this summer, that we will assess.
1986 Terminus Columbia Glacier
2007 Terminus Columbia Glacier
2013 Terminus Columbia Glacier
Jill Pelto painted the glacier as it was in 2009 (top) and then what the area would like without the glacier in the future, at least 50 years in the future (middle), and Jill at the sketching location (bottom), turned 180 degrees to view Blanca Lake. The lake is colored by the glacier flour from Columbia Glacier to the gorgeous shade of jade.


 Clearly the area will still be beautiful and we will gain two new alpine lakes with the loss of the glacier. After making over 200 measurements in 2010 we completed a mass balance map of the glacier as we do each year. This summer we will be back again for the 32nd annual checkup. There will be likely be record low snowpack, comparable to 2005 the worst year from 1984-2014.
Clearly the area will still be beautiful and we will gain two new alpine lakes with the loss of the glacier. After making over 200 measurements in 2010 we completed a mass balance map of the glacier as we do each year. This summer we will be back again for the 32nd annual checkup. There will be likely be record low snowpack, comparable to 2005 the worst year from 1984-2014.
2010 Mass Balance map of Columbia Glacier







 Dean of Academic Affairs at Nichols College and Professor of Environmental Science at Nichols College in Massachusetts since 1989. Glaciologist directing the North Cascade Glacier Climate Project since 1984. This project monitors the mass balance and behavior of more glaciers than any other in North America.
Dean of Academic Affairs at Nichols College and Professor of Environmental Science at Nichols College in Massachusetts since 1989. Glaciologist directing the North Cascade Glacier Climate Project since 1984. This project monitors the mass balance and behavior of more glaciers than any other in North America.
[…] Columbia Glacier occupies a deep cirque above Blanca Lake ranging in altitude from 1400 meters to 1700 meters. Kyes, Monte Cristo and Columbia Peak surround the glacier with summits 700 meters above the glacier. The glacier is the beneficiary of heavy orographic lifting over the surrounding peaks, and heavy avalanching off the same peaks. Standing on the glacier is a bit like being in the bottom of a bath tub, with avalanche slopes extending up both sides, predominantly on the west side. The last half of January 2021 was a dry period in the region, with an extensive crust forming on the snowpack. This was followed by 106 inches of dry snowfall from Feb. 4 to Feb. 20,and then 34 inches of wet snowfall and even rain through Feb. 24 This generated extreme avalanche danger and numerous climax avalanches in the Stevens Pass region. […]